Research Background and Significance
As a third-generation nucleic acid vaccine, mRNA vaccines offer distinct advantages over first-generation inactivated vaccines and second-generation recombinant protein vaccines, including lower costs, higher protection rates, and shorter development and production cycles. However, traditional lipid nanoparticle (LNP) carriers exhibit certain toxicity, limiting the deliverable dose and applicability of mRNA vaccines. To address this critical bottleneck, the research team employed two synergistically interacting ionizable lipids to construct a novel composite LNP delivery system, significantly enhancing endosomal escape efficiency and mRNA expression levels both in vitro and in vivo (Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2424). When loaded with herpes zoster mRNA antigen, this composite LNP induced potent humoral and cellular immune responses lasting over 7 months in multiple mouse models. In guinea pig challenge studies, it demonstrated protective efficacy comparable to the marketed vaccine Shingrix (GSK) without significant adverse reactions. The study also revealed that removing antigen glycosylation sites significantly alters immunogenicity, providing novel structural insights for designing next-generation mRNA vaccines (Adv. Mater. 2023, 2310886). Beyond the herpes zoster vaccine, the research team concurrently advanced mRNA vaccine development targeting Mycoplasma infections, rotavirus, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). All candidates demonstrated promising immunogenicity and application prospects, with potential for further advancement into translational studies.
Core Methods and Technologies
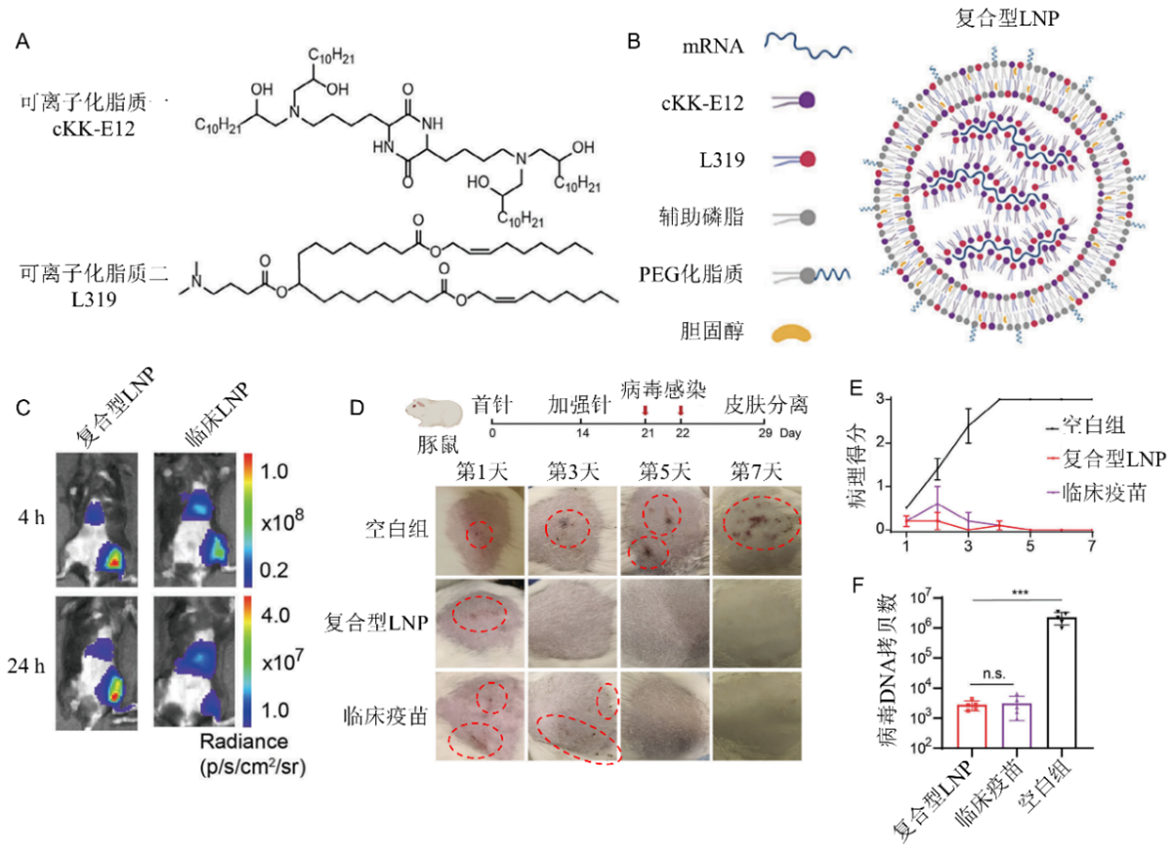
Figure 1. Construction of Composite LNP and Vaccine Efficacy. (A) Ionizable lipid structure of composite LNP; (B) Schematic diagram of composite LNP nanoparticle structure; (C) mRNA expression efficiency after intramuscular injection of composite LNP versus clinical LNP; (D, E, F) Protection against herpes zoster virus infection in guinea pig skin by composite LNP versus clinically approved herpes zoster subunit vaccine.