Research Background and Significance
To address the critical bottlenecks of existing mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)—including strong hepatic accumulation, low local delivery efficiency, and potential hepatotoxicity—the participants developed a novel LNP platform (Eff-isLNP) with in situ targeting and ultrasound responsiveness. Through surface engineering modifications and internal structural remodeling, this system achieves efficient mRNA retention and expression at the lesion site while reducing non-target organ distribution by over 90%. Leveraging the “acoustic imprinting” effect of external ultrasound fields, local mRNA expression is further amplified by 3–8.5-fold. Without inducing systemic inflammation or hepatotoxicity, this approach drives functional angiogenesis in lower limb ischemia models and “angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling” regeneration in critical bone defect models, significantly accelerating tissue repair. This platform establishes a novel paradigm for safe and efficient localized mRNA therapeutics.
Core Methods and Technologies
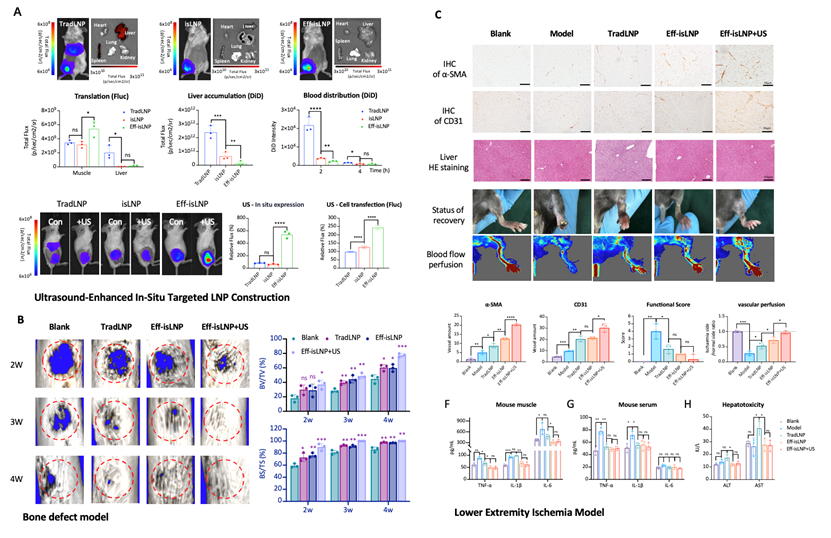
Figure 1. (A) Construction of ultrasound-enhanced in situ targeted Eff-isLNP. This mRNA delivery platform accelerates femoral healing in (B) bone defect models; (C) it accelerates restoration of blood perfusion in lower limb ischemia models while avoiding liver damage.